
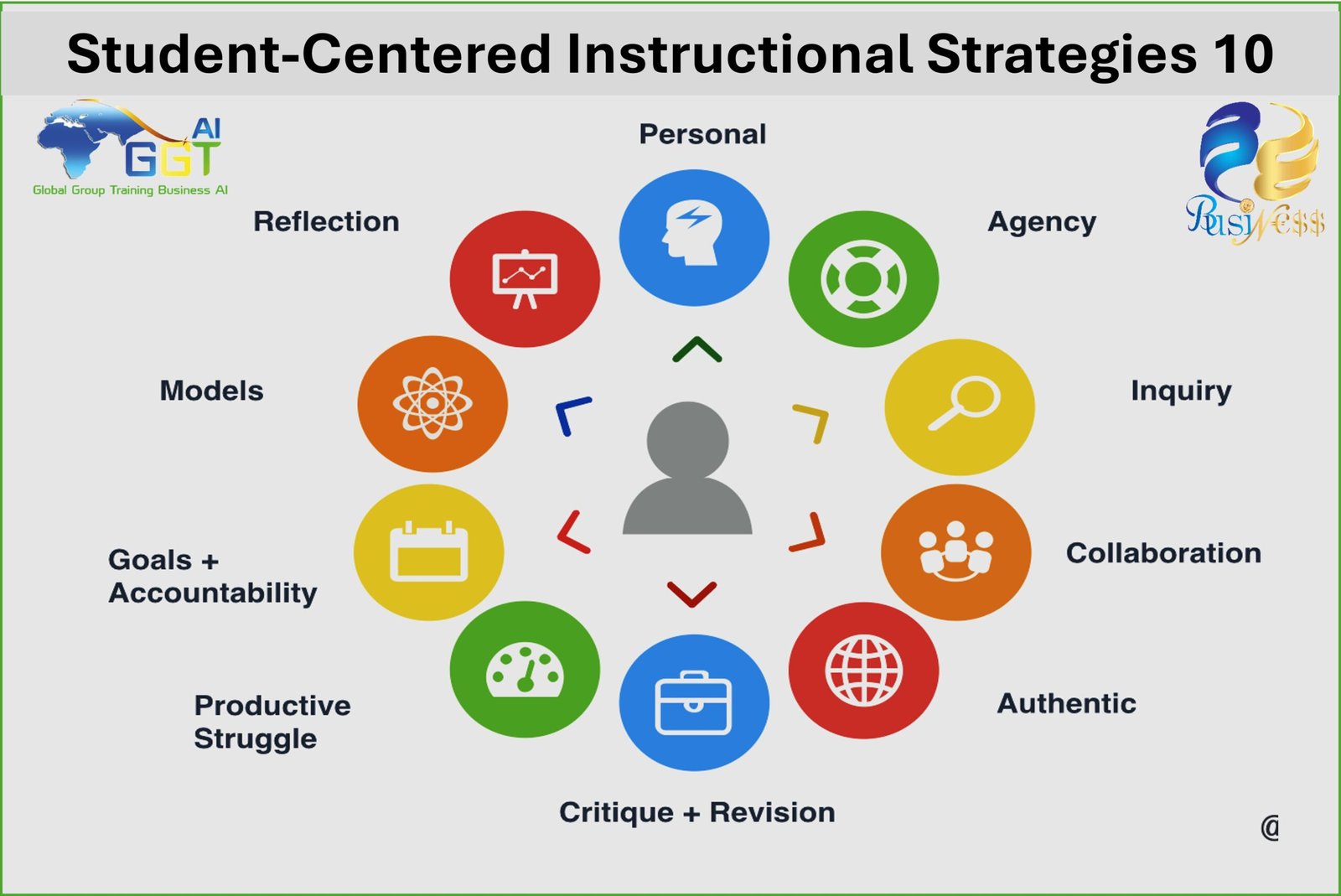
The learning journey is a unique experience for each student. Students have different needs, interests, and learning speeds, making it essential to employ diverse instructional strategies that cater to these differences and focus on the student. In this article, we will explore 28 effective student-centered instructional strategies, explaining each strategy and providing examples of how to implement it in the classroom.
1. Active Learning:
Active learning involves students directly participating in the learning process rather than passively receiving information. This can be achieved through various activities such as group discussions, problem-solving, projects, and role-playing.
2. Cooperative Learning:
Cooperative learning involves students working together in groups to achieve common goals. This helps students develop communication, negotiation, and problem-solving skills, while also fostering a sense of responsibility and belonging.
Self-directed learning involves the student’s ability to guide their own learning and take responsibility for acquiring knowledge. Students can be encouraged to engage in self-directed learning by providing them with diverse learning resources, giving them the opportunity to choose their own topics, and evaluating their own progress.
Project-based learning involves students completing real-world projects relevant to their lives and interests. This helps students apply what they have learned to real-world situations, acquire new skills, and enhance their sense of accomplishment.
Inquiry-based learning involves asking questions and encouraging students to find their own answers. This helps students develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills, and gain knowledge through experimentation and discovery.
Technology-based learning involves using technology in the learning process. Technology can be used for a variety of purposes, such as researching information, communicating with others, creating digital content, and giving presentations.
Differentiated instruction involves providing diverse learning opportunities that meet the needs of all students, regardless of their abilities and learning speeds. This can be achieved by providing different levels of support and challenge, using a variety of teaching strategies, and offering diverse learning resources.
Multisensory learning involves using all the senses in the learning process, such as sight, hearing, touch, smell, and taste. This helps students learn more effectively and retain information better.
Place-based learning involves learning in different environments outside the classroom, such as museums, exhibitions, and community sites. This helps students connect what they have learned to the real world and gain new skills.
Storytelling-based learning involves using stories and narratives in the learning process. This helps students relate information to familiar concepts and develop communication and critical thinking skills.
Analysis and Benefits of Student-Centered Learning Strategies:
Student-centered learning strategies offer numerous benefits for both students and teachers.
Benefits for Students:
Benefits for Teachers:





